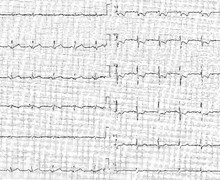
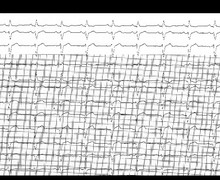
Ventricular undersensing
Tracing
Manufacturer Boston Scientific
Device PM
Field Sensing
N° 1
Patient
- 80-year-old man
- Vitalio pacemaker (Boston Scientific) for sinus dysfunction
- Episodes classified as Rythmiq in the device memory
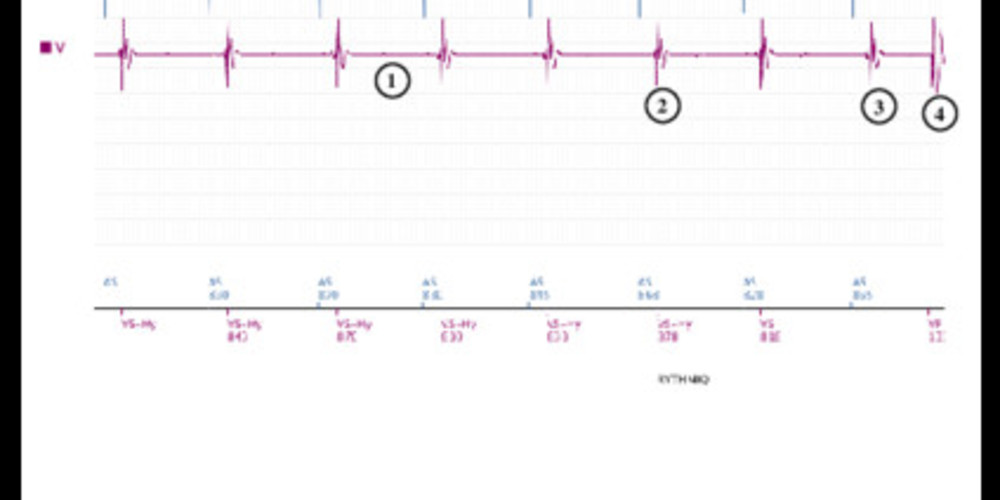
Graph and trace
- Ventricular undersensing
- Ventricular backup pacing as a result of this undersensing
- Second ventricular backup pacing
- Ventricular undersensing and ventricular backup pacing
- Switch to DDD mode (RYTHMIQ)
Comments
- This tracing illustrates a case of ventricular undersensing revealed by the presence of a RYTHMIQ switch
- Ventricular undersensing is followed by backup pacing and switch to DDD mode
- A good quality ventricular sensing, atrial sensing and atrial pacing is required for the RYTHMIQ algorithm to work properly
- Recording an EGM in case of switch to DDD allows the diagnosis of even intermittent dysfunctions
- Traditionally, unlike ICDs, pacemakers functioned with a fixed and stable sensitivity throughout the cardiac cycle
- Modern pacemakers allow the programming of an ICD-like adaptive sensitivity (variable sensitivity levels according to the amplitude of the R wave or the sensed P wave with progressive increase in sensitivity during the cardiac cycle)
- In Boston ScientificTM pacemakers, the 2 options are available: fixed sensitivity or adaptive sensitivity (automatic gain control, AGC)
- The type of sensing method used (AGC or Fixed) must be the same for both leads
- Atrial and ventricular sensitivity values can be programmed independently
- If sensing is programmed on AGC, the nominal sensitivity value is 0.6 mV for the ventricle and 0.25 mV for the atrium
Other articles that may be of interest to you