Atrial sensing failure
Tracing
Manufacturer Medtronic
Device PM
Field Pacing & Sensing
N° 16
Patient
69-year-old man with complete atrioventricular block and post-surgical replacement of an aortic valve; numerous episodes of atrial arrhythmia in the postoperative phase; control 1 month post-implantation.
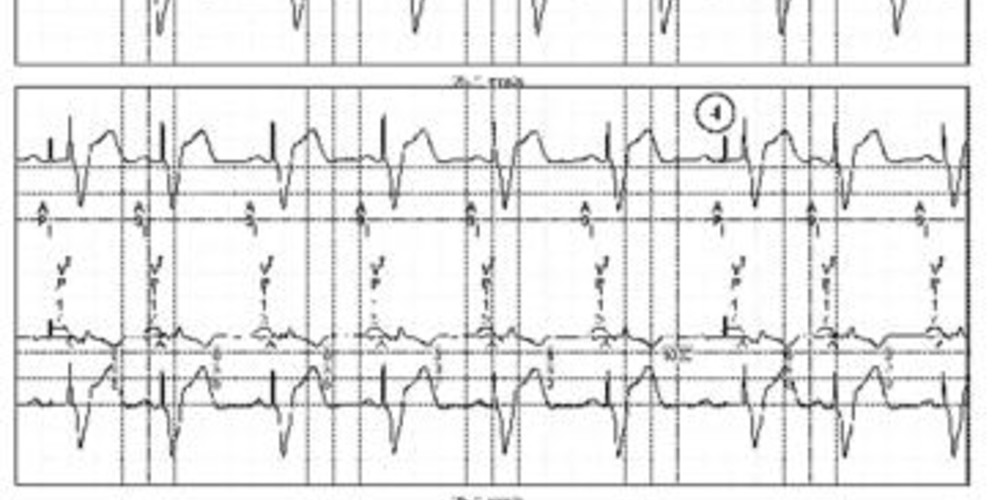
Graph and trace
The first line corresponds to lead II, the second line to the markers, the third line to lead III with the superimposed intervals and the last line to lead I;
- P wave visible on the various leads not detected by the device;
- atrial pacing at the end of the escape period; this pacing occurs in the vulnerable period of the previous undetected P wave; ventricular pacing;
- proper atrial sensing and ventricular pacing (AS-VP);
- new atrial undersensing.
Other articles that may be of interest to you




This tracing reveals an intermittent atrial undersensing. The quality of the sensing of a signal is contingent on a certain number of its physical characteristics:
The sensing of the P wave presents certain peculiarities. Indeed, the amplitude of the sensed atrial signal may vary according to the position of the patient and as a function of the respiratory cycle. It is therefore necessary to set a sufficient margin to avoid the problems of atrial undersensing on exertion which, in a patient with an atrioventricular block, may cause a sudden drop in ventricular pacing rate. In addition to the lack of proper monitoring of P waves upon exertion, atrial undersensing may have a pro-arrhythmogenic effect if atrial pacing occurs in an atrial vulnerable period with a risk of atrial arrhythmia induction.