Cross-talk and inappropriate mode switch
Tracing
Manufacturer Boston Scientific
Device CRT
Field Management of atrial arrhythmias
N° 8
Patient
56-year old male patient with a history of severe ischemic cardiomyopathy with left bundle branch block was implanted with a triple-chamber Boston Scientific Autogen CRT-D. Interrogation revealed an episode of mode switch (RTA).
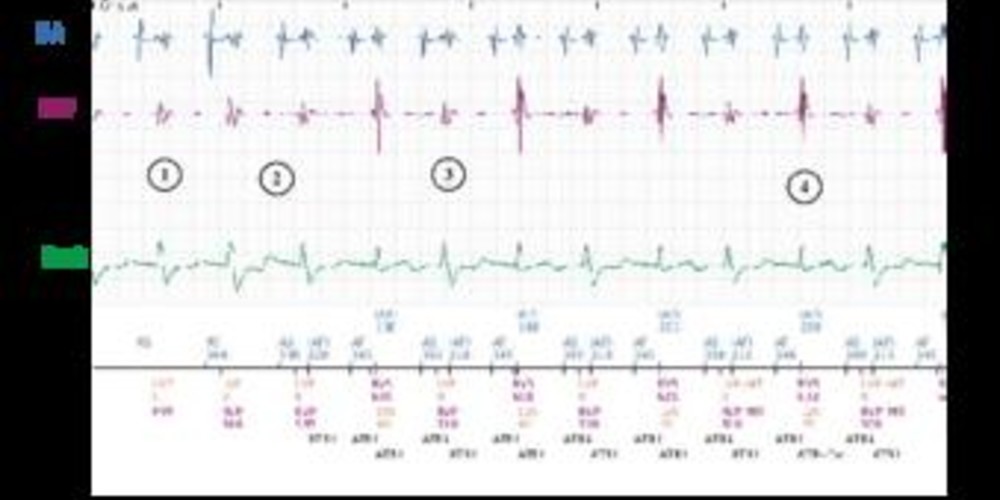
Graph and trace
- Atrial sensing and biventricular stimulation.
- Cross-talk with oversensing of ventricular depolarization by the atrial lead.
- Prolonged oversensing with cycles classified as AF.
- After 8 atrial cycles faster than the programmed atrial tachycardia threshold (entry counter programmed at 8 cycles), the entry counter is complete and the duration begins (ATR-Dur).
- After 8 ventricular cycles (programmed at 8 cycles) mode switch to asynchronous DDI mode with fallback (ATR-FB).
- When oversensing terminates, the exit counter is completed (programmed at 8), the device switches back to a synchronous mode.
- New mode switch related to cross-talk.
Other articles that may be of interest to you
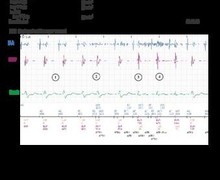




Cross-talk with alternans between 2 different signal morphologies and amplitudes. An alternans between cycles is also seen (the first at approximately 220ms corresponds with oversensing while the second is at approximately 350 ms).
The atrial blanking post ventricular stimulation is the preferred parameter to regulate to correct this problem. The blanking may be programmed ‘SMART’ or at a fixed value. Boston Scientific devices have a different atrial blanking for post-stimulation and for post-detection.
Programming SMART aims to reduce blanking durations while reducing the risk of cross-talk, disabling the noise window in the blanking period and raising the gain threshold to avoid cross-talk (CAG raised to 3/8 of the measured conducted peak in order to diminish sensibility).
In the case of cross-talk, it may be preferable to program a fixed value of atrial blanking post ventricular stimulation to avoid oversensing. When it is not possible to correct the oversensing within acceptable refractory periods, it is possible to modify the atrial sensitivity while trying to respect a sufficient margin in order to detect atrial signals in sinus rhythm and during arrhythmia.