Sinus tachycardia, anti-PMT algorithm and pro-arrhythmogenic effect
Tracing
Manufacturer Boston Scientific
Device CRT
Field Effort
N° 5
Patient
A 51-year old male patient with a history of ischemic cardiomyopathy with left bundle branch block was implanted with a triple-chamber Boston Scientific Incepta CRT-D. Interrogation revealed PMT and VT episodes.
Graph and trace
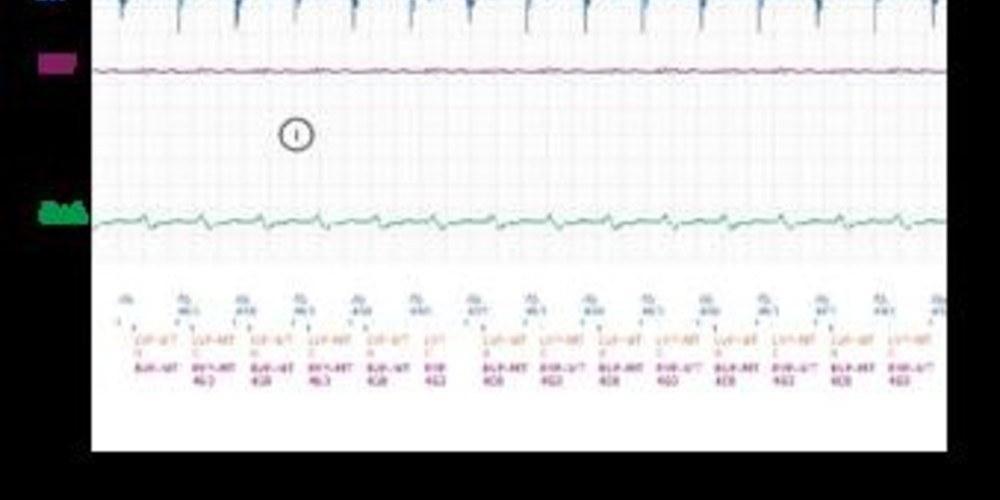
- atrial sensing and biventricular stimulation at maximal rate.
- since there are 16 consecutive AS – BV cycles at the maximal tracking rate with a stable BV – AS interval, the device diagnoses a PMT (PMT-B).
- prolongation of the PVARP to 500 ms for one cycle; atrial activity occurs within the PVARP which inhibits triggering an atrioventricular delay; sensing of intrinsic ventricular activity with left bundle branch block.
- continuation of sinus tachycardia; right ventricular stimulation with long AV delay in order to not surpass the maximal rate; inhibition of left ventricular stimulation since the interval between preceding left ventricular detection and the intended left ventricular stimulation is too short.
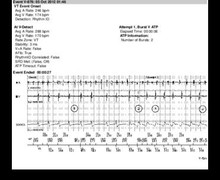
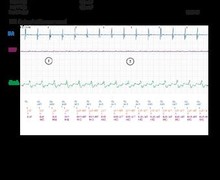
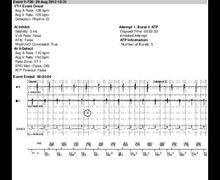
- onset of a ventricular tachycardia detected in the VT zone.
- after the end of the duration, the first ATP sequence is delivered (burst).
- unsuccessful burst with continuation of the VT.
- second burst.
- continuation of the VT.
- third burst.
- continuation of the VT.
- first ramp.
- successful ramp with cessation of the VT, sinus tachycardia continues.
Other articles that may be of interest to you




This EGM illustrates the risk of inducing ventricular arrhythmia in certain patients after a non-conducted P wave and the succession of long – short cycle during exercise (in this case triggered by an inappropriate intervention by the anti-PMT algorithm). For Boston Scientific devices, the diagnosis of a PMT can only occur during maximal tracking rate. Therefore it is important to program this parameter carefully since it influences not only the ability of biventricular stimulation during maximal exercise but also PMT diagnostics (when the maximal tracking rate is programmed at 150 bpm, there will be no PMT diagnoses at slower heart rates). When the patients reaches the maximal tracking rate, 1 in 16 atrial activities will be non-conducted due to this algorithm (16 AS – VP cycles trigger a PMT diagnosis) which can be (in exceptional cases) pro-arrhythmogenic.
In this patient, who never showed any signs of true PMT, we have raised the maximal tracking rate and disabled the anti-PMT algorithm.